A supernova flash is an astronomical phenomenon in which a star sharply increases its brightness and then slowly fades. This was reported by Naked science magazine.
In the distant 1572, an explosion of an unusually bright star with the naked eye was observed in the night sky. She was noticed by a scientist from Denmark, Tycho Brahe. The object was located in the constellation Cassiopeia about 7500 light years from Earth. The star was named after this Danish astronomer. Since then, this is the first supernova explosion that has been observed by man. Interestingly, its maximum magnitude was -4. The scientist compared its brightness to Jupiter, and after its gradual decay, with closely spaced stars.
Tycho Brahe published the results of his research in his work Essays on New Astronomy at the beginning of the 17th century. Similar observations were made by English scientists. They also admitted that such stars can be anywhere in the universe.
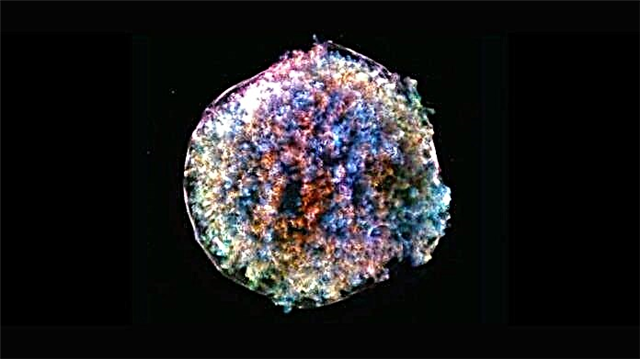
But from now on, the remains of an astronomical object do not give peace to astronomers. It turns out that SN 1572 has no similarities with similar astronomical objects. Computer models help determine the cause of such discrepancies. Tycho Brahe is a double star that belongs to the class Ia. Such stars form when the white dwarf begins to absorb so much material from its double that the thermonuclear reaction begins to work.In the process, a dwarf star explodes.
The remains of a white dwarf are a sphere with smooth or bent edges. But further observations of the supernova revealed that its trace looked like crumpled paper. For a long time, scientists could not find the cause of this phenomenon. According to x-ray studies, it became clear that the Tycho remnants have a spherical shape with an uneven surface.
So far, two variants of the nature of this phenomenon are being discussed: either deviations from the spherical shape occurred at the beginning of the explosion, or this happened after the supernova explosion. To clarify the circumstances of the changes in the supernova, a team of scientists conducted a series of computer simulations. They conducted them in two versions: as if irregularities had formed at the beginning of the explosion and as a slow explosion with the formation of uneven lumps later.
According to the simulation results, irregularities in the sphere could appear at the beginning of the outbreak. This would be possible if the explosion occurred at once at several points of the star’s core. Recent studies show that two white dwarfs located at a relatively short distance can behave like Tycho. The total mass in this case will be more than the Chandrasekhar limit (the upper limit at which a white dwarf can still exist).
The introduction of new technologies during astronomical research will help to unravel the nature of supernovae like Tycho Brahe.